
PARTS OF AN EARTHQUAKE

FOCUS
It is the location where the earthquake begins. The ground ruptures at this spot, then seismic waves radiate outward in all directions. The focus is also called the hypocenter of an earthquake.
FAULT
It is a planar fracture in a volume of rock, across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movement, some faults can result from the action of plate tectonic forces.
EPICENTER
It is the point on the Earth's surface that is directly above the hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or underground explosion originates and in most cases, it is the area of greatest damage.
SEISMIC WAVES
These are the waves of energy caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the earth. They are the energy that travels through the earth and is recorded on seismographs.
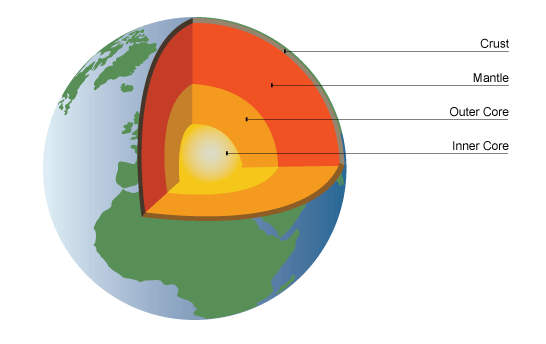
EARTH MOVEMENT
Movement in the crust of the Earth is the cause of an earthquake. The Earth is made of four major layers: the inner core, the outer core, the mantle, and the crust which is the surface of the Earth that includes all the oceans and continents. The crust is made of tectonic plates which lie on the mantle. As these plates move around, some slide horizontally, some push together and force the ground upward, slide beneath another plate, or pull apart. Whenever tectonic plates suddenly move, this causes an earthquake to occur. When two parts of the earth's surface move, the rock catch on each other.
The rocks are just pushing each other but they are not moving. After that, the rocks break because of the pressure, and then the earthquake occurs. Earthquake waves cause movement in the surrounding areas because of air pressure and imbalance. Because of the release of elastic energy after forceful tectonic plate movements, the earthquake will be the result. Tectonic plate is the reason for the formation of mountain, earthquake and volcanoes. The energy that is released in the earth's crust can cause by a sudden dislocation of segments of the crust.
PLATE TECTONICS
DIVERGENT BOUNDARY

A divergent boundary is a fault where two plates are moving away from each other. The movement of these plates are caused by convective forces in the magma below them. When this occurs in a continental place a rift valley is formed. On the other hand, a ridge is formed when it occurs within the oceanic plates.
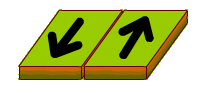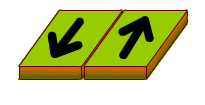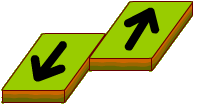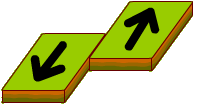
TRANSFORM BOUNDARY
When plates are sliding past one another this is called the transform boundary. When this occurs, crust it neither destroyed nor created along them This commonly happens on the seafloor where oceanic fracture zones are created. When it occurs on land, it produces faults.
CONVERGENT BOUNDARY
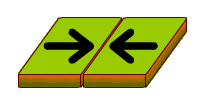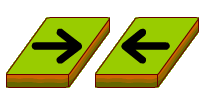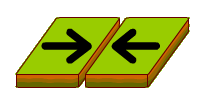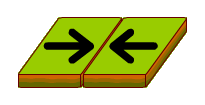
Convergent boundary happens when plates move towards each other and collide. When a continental plate collides with an oceanic plate, the oceanic plate sinks beneath the more rigid continental plate and this is called subduction.
This results to the creation of mountains and trenches such as the one occurring between the Nazca Plate and the South American plate, resulting to the Andes mountains and the Peru-Chile trench. In the case where to oceanic plates collide. A deep trench will be formed such as the Marianas trench. Lastly, when continental plates collide with each other, they are pressed together with intense pressure since they can’t subduct. This process can lead to the formation of huge, high mountain rages such as the Himalayas.